728x90
반응형
모두를 위한 딥러닝 강좌 시즌 1
by Sung Kim, 김성훈 교수님
링크
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qPMeuL2LIqY&list=PLlMkM4tgfjnLSOjrEJN31gZATbcj_MpUm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-57Ne86Ia8w&list=PLlMkM4tgfjnLSOjrEJN31gZATbcj_MpUm&index=3
01. Machine Learning 용어와 개념 설명
머신러닝이란?
반응형 프로그램의 한계를 극복하기 위함.
ex) 스팸메일의 구분을 위해 일일히 케이스를 분류하기 어려움.
개발자가 케이스를 지정해주는 것이 아닌 프로그램 자체가 학습하는 영역을 갖는 프로그램
학습방법에 따라
- Supervised learning : training set(labeled examples) 을 통해 학습을 진행
- Unsupervised learning : un-labeled data를 통한 학습
- 뉴스 그룹핑
- 단어 클러스터링
Supervised learning
머신러닝의 common problem type
- Image labeling
- Email spam filter
- Predicting exam score
유형
- 회귀(regression) : 특정 범위 상의 값을 찾는 문제
- 이진 분류(binary classification) : 두 개 중 하나를 고르는 문제
- 다형 분류(multi-label classification) : 여러 개의 유형 중 하나를 고르는 문제
01. TensorFlow의 설치 및 기본적인 operations
Tensorflow : 구글에서 만든 오픈소스 라이브러리
- 가장 많은 사람들이 사용하기 때문에 공부하기 좋은 라이브러리이다.
- data flow graph를 사용해서 numerical 계산을 할 수 있다.
- python에서 사용 가능하다
- Data flow graph : 노드와 노드가 연결된 일련의 계산과정을 그래프로 나타낸 것
텐서플로우 설치
pip install --upgrade tensorflow # cmd 창에서 설치
import tensorflow as tf
tf.__version__ # tensorflow 버전 확인
가장 기초적인 tf 사용
# Create a constant op
# This op is added as a node to the default graph
hello = tf.constant("Hello, TensorFlow!")
# start a TF session
sess = tf.Session()
# run the op and get result
print(sess.run(hello))- 그래프 상에 하나의 노드를 만들고, 세션을 만들어서 노드를 실행
더하기로 연결된 노드 구현
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32)
node2 = tf.constant(4.0) # also tf.float32 implicitly
node3 = tf.add(node1, node2)
print("node1:", node1, "node2:", node2)
print("node3: ", node3)sess = tf.Session()
print("sess.run(node1, node2): ", sess.run([node1, node2]))
print("sess.run(node3): ", sess.run(node3))- 더하기 과정을 실행하고 싶다면 세션을 만들어야 함
Tensorflow 매커니즘
- tf를 이용해 data graph를 빌드
- sess.run(op)을 통해 그래프를 실행 (op : operation)
- 그래프 값들을 업데이트 하거나 결과값을 출력
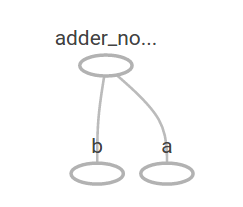
Placeholder
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node = a + b # + provides a shortcut for tf.add(a, b)
print(sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: 3, b: 4.5})) # 1개의 값
print(sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: [1,3], b: [2, 4]})) # 2개(n개)의 값- 실제 값을 모를 때에도 노드를 만들 수 있다
- n개의 값을 동시에 넘기는것도 가능
Tensor의 Rank, Shape, Type
3 # a rank 0 tensor; this is a scalar with shape []
[1. ,2., 3.] # a rank 1 tensor; this is a vector with shape [3]
[[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]] # a rank 2 tensor; a matrix with shape [2, 3]
[[[1., 2., 3.]], [[7., 8., 9.]]] # a rank 3 tensor with shape [2, 1, 3]- rank는 차원으로 이해하면 된다
- shape의 [m, n, l]
- m : 1차원에서 요소의 개수
- n : 2차원에서 요소의 개수
- l : 3차원에서 요소의 개수
'Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [네이버 부스트코스] 모두를 위한 데이터 사이언스 (0) | 2022.01.03 |
|---|---|
| [모두를 위한 딥러닝] 02_Linear Regression (0) | 2021.12.08 |